Task 4 - Assesment of Environmental Effects and Monitoring Efforts
|
OBJECTIVES The third phase of Annex IV was approved by the OES ExCo in May 2016. This phase builds on the work completed during the first two phases by continuing to collect, synthesize, and disseminate information on environmental effects and by providing access to such knowledge and information related to research, monitoring, and evaluation of environmental effects of MRE information that helps advance the MRE industry. Annex IV is supported by the publicly accessible, online knowledge management system Tethys, developed by Pacific Northwest National Laboratory. Tethys was created to provide a commons for Annex IV and to facilitate connectivity and collaboration among members of the MRE community. Tethys hosts a knowledge base and map viewer providing access to MRE documents, archived webinars, and other media that are focused on important scientific issues critical to the siting and permitting (consenting) of MRE devices worldwide. Annex IV also plays a role in supporting the dissemination of information via international conferences and events, as well as focusing on new environmental research and data on interactions among marine animals, habitats, and MRE devices. Annex IV is characterized by the close involvement of an analyst from each of the 15 member nations. Each analyst was nominated by his/her nation and is committed to contributing 20 hours per quarter to Annex IV. |
PROJECT DURATION
|
MEMBER NATION ANALYSTS
Key tasks asked of each analyst include:
- Reporting progress in MRE development and environmental effects work within their respective countries, updating existing Annex IV metadata forms, and providing new ones as projects or research studies are initiated;
- Acting as an expert to help identify topics for Annex IV webinars, expert forums, and workshop topics;
- Providing reviews of Annex IV products and Tethys content;
- Acting as an ambassador for Annex IV in their respective country;
- Translating key Annex IV documents from English into the official language of their respective country.
THE ROAD TO RETIRING ENVIRONMENTAL RISKS
During 2018 Annex IV pursued a process for retiring, or putting aside, environmental risks that continue to slow consenting and hamper MRE development. Regulators around the world continue to require that a significant amount of data be collected to determine the effects of devices and systems on marine animals, habitats, and ecosystems. The collection of pre- and post-installation monitoring data places substantial cost burdens on device and project developers, threatening the financial viability of this young industry. The risk retirement process is made up of three parts: 1) Data Transferability and Data
Collection Consistency; 2) Risk Retirement Pathway; and 3) Outreach and Engagement with the MRE Community. Data Transferability and Data Collection Consistency - A process has been developed to systematically collect, classify, and enhance discoverability of datasets from already consented projects. These datasets will be made accessible to regulators, developers, and other stakeholders. The purpose of these datasets is to provide lessons learned from consented projects to simplify and reduce the need for extensive data collection on new consenting and licensing applications. As part of classifying datasets, there is a need to ensure that environmental data are collected in a consistent manner for future applications. The process is shown graphically (Figure 5).
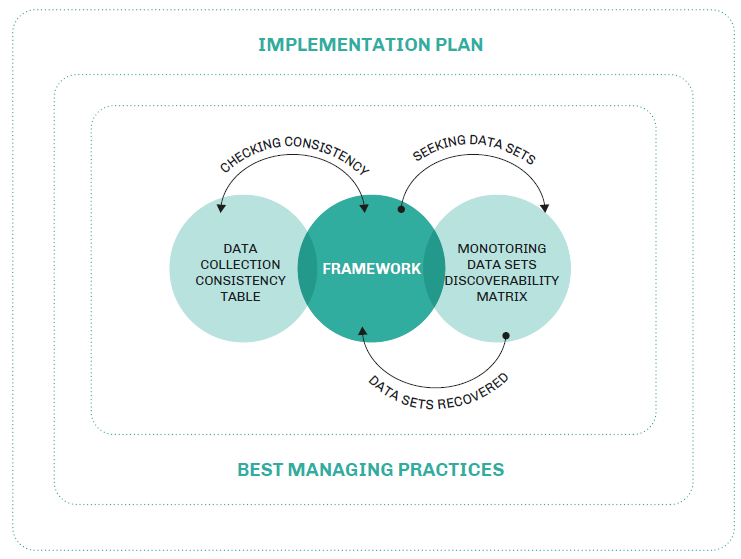
Data Transferability Framework (Framework) is made up of: 1) Data Collection Consistency Table which provides preferred measurement methods or processes, reporting units, and the most common methods of analysis or interpretation/use of data; 2) Monitoring Data Sets Discoverability Matrix which allows a practitioner to discover data sets that meet the criteria presented in the Framework; 3) Best Management Practices includes five BMPs related to data transferability and collection consistency; and 4) Implementation Plan which is the approach for implementing the Framework and BMPs.
Risk Retirement Pathway
A draft risk retirement pathway has been developed and shared with the Annex IV analysts. The pathway
describes the necessary steps to retire a specific risk, which includes “offramps” that allow the risk to be put aside as not likely to cause harm to marine animals or their environment. The process can be applied to any specific environmental risk such as collision risk with turbine blades, effects of underwater noise on animals, electromagnetic fields, etc. Application of this pathway will be explored in greater detail in the 2020 State of the Science Report.
Outreach and Engagement with the MRE Community
Following the survey of US regulators carried out in 2017, several additional Annex IV countries have surveyed their national regulators. The purpose of the surveys is to understand which risks from MRE development the regulators feel are most important, to guide tailored outreach programs to ensure regulators are familiar with existing scientific information, and to determine the most appropriate methods for engaging them in discussions of risk retirement and requests for monitoring data that are proportional to risks. During 2018, a substantial program of outreach and engagement was carried out with US regulators through a series of in person and online meetings that demonstrated the state of knowledge for key environmental risks of importance to US regulators (collision risk, underwater noise, EMF, habitat changes, and changes to physical systems such as circulation and sediment transport). During each meeting, regulators were asked to assess the state of knowledge as it applied to their jurisdictions and to discuss what additional data or analysis they might need to move forward. The regulators were also introduced to the data transferability process, asked for input, and encouraged to explore the work further. In particular, the regulators were enthusiastic about the development of the dataset discoverability matrix (Fig.5) that would allow them to access, categorize, and apply datasets from consented projects. The same process will be carried out in other Annex IV countries as the results of the regulator surveys become available. A workshop on the data transferability process will engage the international community in September 2019.
DISSEMINATION OF INFORMATION ON ENVIRONMENTAL EFFECTS
Tethys, the online knowledge management system which supports Annex IV material, continues to expand and increase user interactions. The publicly available collection of scientific papers, reports, and other media increased by 681 papers in the last year, for a total of 4,723 entries. The collection includes information on offshore wind effects as well, but a large portion of the papers are exclusively about marine energy development. Over the past year, Tethys has been visited by 53,926 users, viewing 129,984 pages (note these numbers often represent users who visit multiple times).
During 2018, a peer review process was completed for Tethys by soliciting reviews and feedback on the content and functionality of Tethys from the greater Tethys community online. A total of 119 reviews were collected. Respondents rated the value that they derive from using Tethys as an 8.2 on a scale of 1 to 10. The results of the peer review help understand how users interact with the website and provide a guide to improvements and changes to the system.
WORKSHOPS AND CONFERENCES
During 2018, Annex IV hosted two workshops. The first was held in April in conjunction with the Environmental Interactions of Marine Renewables (EIMR) conference in Orkney, UK on social and economic data needed to address consenting. This was a follow on workshop from one held around the European Wave and Tidal Energy Conference (EWTEC) in 2017. Approximately 30 participants came together to examine case studies of social and economic issues surrounding consenting of MRE projects in Europe and North America. The output of the two workshops led to development of a document on best management practices for tracking social and economic data, and a Short Science Summary on the topic (https://tethys.pnnl.gov/socio-econ).
The second workshop was held in conjunction with the International Conference on Ocean Energy (ICOE) in Cherbourg France in June 2018, focused on the data transferability and data collection consistency processes. Over 20 people from seven countries participated. The output of the workshop included a short workshop report, as well as providing important guidance and examples for the data transferability process.
Papers were presented at a number of conferences in 2018 that focused on Annex IV work including papers on data transferability at EIMR (April 2018), Marine Energy Technology Symposium (METS) in Washington DC in May, at ICOE (June 2018), and at AWTEC (September 2018). An extended paper on the 2016 State of the Science report findings was also presented at AWTEC.
WEBINARS
Three webinars were hosted by Annex IV during 2018. The first focused on direct outreach for Tethys, ensuring that new users understood the resource as well as introducing new features to more experienced users 49 people attended in person and 387 have downloaded the presentation since. The second webinar Optimizing Permitting for MRE through Data Transferability, was held September 25th, and reported on the work that Annex IV has been doing on regulator outreach over the year. 37 people attended and 173 have downloaded the presentation since. In addition, Annex IV sponsored a webinar: Using Underwater Video to Monitor Fish Around Ocean and River Energy Devices in July 2018 that 47 people attended, and 245 downloaded later. Webinar presentations are archived at: http://tethys.pnnl.gov/mhk-environmental-webinars.
COLLECTION AND UPDATE OF METADATA
The purpose of the metadata forms is to ensure that the sum of environmental monitoring data from all deployments anywhere in the world is captured and added to the global knowledge of MRE environmental effects. Building on the collection of metadata from phases 1 and 2, Annex IV has continued to collect and update information on new wave and tidal projects as well as ongoing research studies. Existing metadata forms are updated by working with the country analysts, developers, researchers. There are a total of 158 metadata forms on Tethys; of those 64 are considered to be active projects while the rest represent short term deployments with no follow up or projects that have been withdrawn. Six new project forms were added during 2018. All metadata forms can be found on Tethys under the Knowledge Base.
PREPARING FOR THE 2020 STATE OF THE SCIENCE
The major output of Annex IV Phase 3 will be the 2020 State of the Science report. Preparations for the report began in late 2018 with discussions over a report outline and chapter authorship with the Annex IV analysts.
FUTURE ACTIVITIES
Future efforts for Phase 3 will focus on developing the 2020 State of the Science report and completing the process of risk retirement. A workshop is planned around EWTEC 2019 in Naples Italy to test retirement of two stressors (underwater sound effects and electromagnetic fields). A workshop is also planned for Scotland in February 2019 to further the strategic research agenda towards retiring collision risk with turbines.
Annex IV expects to have a presence at several conferences including: METS (Marine Energy Technology Symposium) in the US in April 2019 and EWTEC in Naples in September 2019.
CHANGES TO ANNEX IV BRANDING
Beginning in early 2019, Annex IV will be rebranded as OES-Environmental, to more closely reflect the international ties to OES